Functions of the Heart
- The right heart collects deoxygenated blood from the entire body and sends it to the lungs to be loaded with oxygen again
- The left heart pumps oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the entire body
- The pacemaker (SA Node) sets the electrical rhythm for the heart to pump blood
- Blood carries nutrients, gases, and wastes to and from the body
Layers of the Heart
The heart can be divided into 3 layers from the outside to the inside: Pericardium (thin layer), Myocardium (thick layer), and Endocardium (thin layer)

Chambers of the Heart
The heart has 4 chambers. The top chambers are called the atria (right atrium and left atrium). The bottom two are called the ventricles (right ventricle and left ventricle). The septum divides the atrium and ventricles into the right and left sections.
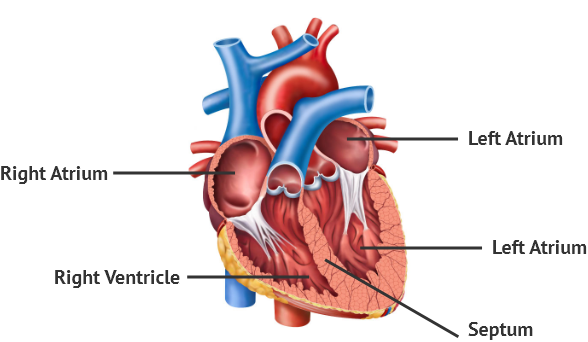
The heart has 4 chambers. The top chambers are called the atria (right atrium and left atrium). The bottom two are called the ventricles (right ventricle and left ventricle). The septum divides the atrium and ventricles into the right and left sections.
The heart is positioned at an angle, tilted to the right. The left side of the heart is more muscular and larger than the right side since it squeezes blood out to the entire body.
Major Blood Vessels of the Heart
Arteries are the blood vessels that deliver the oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the whole body. Veins are the blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart. However, the Pulmonary Artery and Veins are the only exceptions to this rule.
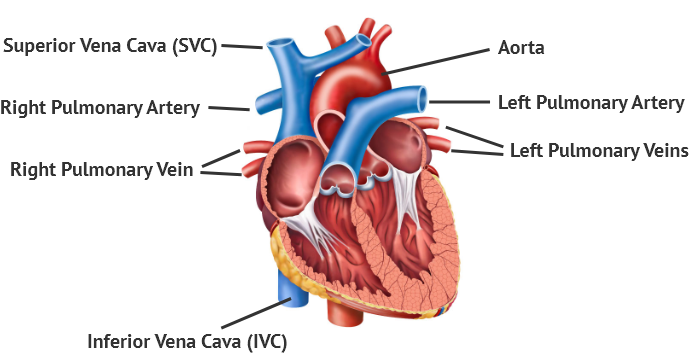
Superior Vena Cava (SVC) & Inferior Vena Cava – bring the deoxygenated blood from the head, neck, and the rest of the body into the right atrium. They are the largest veins in the body.
Right & Left Pulmonary Arteries – bring the deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle into the lungs
Right & Left Pulmonary Veins – bring the oxygen-rich blood from the lungs into the left atrium
Aorta – brings the oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle to the rest of the body. It is the largest artery in the body.
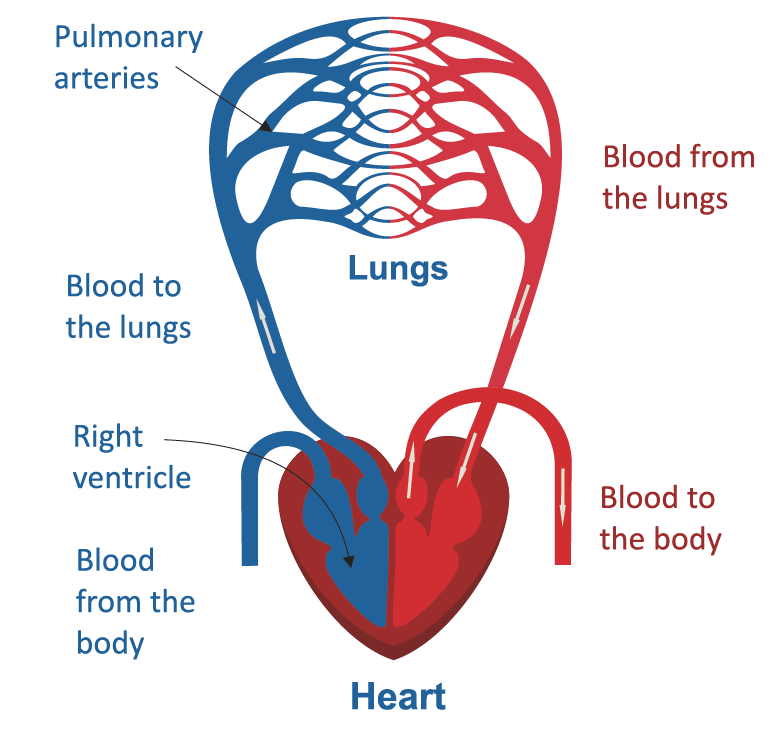
How the Blood Flows through the Heart
The heart can be divided into right and left halves. The right heart brings the de-oxygenated blood collected from the veins from all over the body and returns it to the lungs where it is reloaded with fresh oxygen. The oxygen-rich blood then reaches the left heart and is pushed out to the rest of the body.
Valves of the Heart
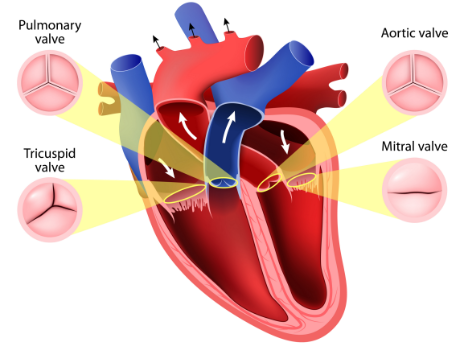
The Tricuspid Valve – controls the blood flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle. It has three leaflets.
The Pulmonic Valve (also called the semilunar or bicuspid valve) – controls the blood flow from the right ventricle to the lungs. It has three leaflets.
The Mitral Valve – controls the blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle. It has two leaflets.
The Aortic Valve – controls the blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta. It has three leaflets.
Blood Supply of the Heart
The blood supply to the heart is called coronary circulation. Although the heart is the organ that pumps blood out to the whole body, it needs to be supplied by a set of blood vessels to function, The coronary arteries are the major blood vessels that supply blood to the heart muscles.
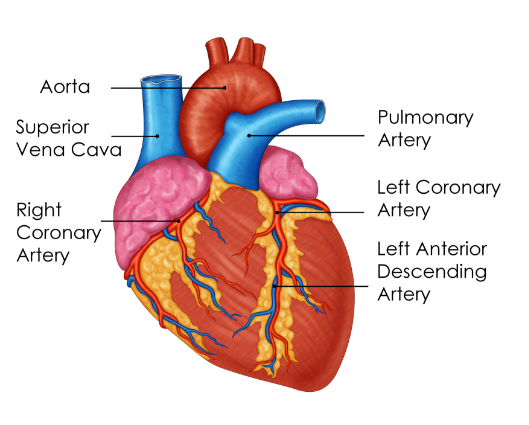
Some main arteries and branches:
- Right Coronary Artery – supplies the right side of the heart including the Sinoatrial (SA) & Atrioventricular (AV) nodes
- Left Main Coronary Artery – supplies the back of the heart
- Left Anterior Descending Artery – supplies the front and left side of the heart
- Circumflex Artery – supplies the back and outer areas of the heart
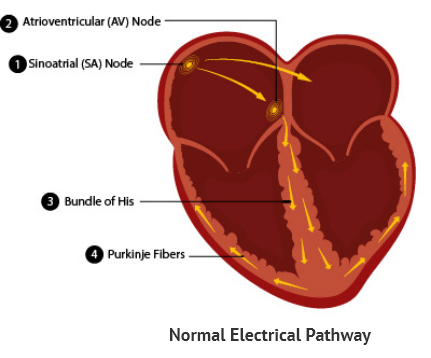
The Electrical Pathway of the Heart
The heart has an inbuilt electric circuit that gives the heart the energy to pump blood to the various organs of the body. The Sinoatrial Node (also called SA Node or the Pacemaker) is where the electrical impulse starts and it continues to Atrioventricular Node (AV Node) and to the rest heart in a set pattern. Due to the electrical pulses the heart muscles squeeze and relax in an organized manner causing the blood to keep moving throughout the body.
Electric Pathway: SA Node → AV Node → Bundle of His → Purkinje Fibers